 值得信赖的区块链资讯!
值得信赖的区块链资讯!
Dissolving the Myths of Crypto Mining – Part 1
Way before we knew about crypto, we knew about mining. The undeniable buzz surrounding the mining business has been pretty overwhelming. If you ask your next door neighbor to explain what miners do your might hear something along these lines — mining is something that earns you a lot of cash, you just have to solve some puzzles, it burns a lot of electricity, so on and so forth. Sounds intriguing, does not it? It certainly does, however, and sadly so, this description can be pretty misleading. The following blog aims to decrypt all the myths associated with crypto mining and investigate who miners are, how do they get involved and what their business strategies and operations look like.

Miners
Mining plays a significant role behind seamless digital asset transaction: it validates the transfers, generates and stores blocks and reaches consensus upon which blocks to be included in the blockchain string. But what exactly do miners do?
The biggest misconception there exists is that miners are individuals who sit at their computers and solve complicated mathematical puzzles around the clock. The truth is that not miners but the computers with the special embedded software automatically run and solve the puzzles by pairing transaction hash with the matching hash. There is no need for a human to be sitting at the computer, as the software does everything autonomously. What humans do is that they engage in mining for pure economic interest and simply contribute their computational power to mining by purchasing/renting the special machines and incurring the electricity and cooling costs.
The special mining hardware is an advanced high-level equipment used to make speedy complicated computations on the blockchain. For a high-quality hardware, price tag ranges between $636-$3,000, depending on performance and energy-consumption properties. In addition to the upfront costs of equipment installation, recurring big energy bills also add up to miners’ expenses, as mining consumes a lot of power. What is more, the hardware has short lifetime value — as the mining difficulty constantly increases, once superior technology might quickly become obsolete and idle.

As of today, professional mining companies dominate the industry. They produce special equipment and either sell or rent them to the interested parties. Some of them also have large mining farms — data centers equipped with superior technology that continuously mine different cryptocurrencies. These farms are usually located in favorable settings and enjoy a low cost of electricity to decrease monthly electric bills, high network speed to make speedy operations and cool climate to keep cooling costs minimal.
Individuals who want to get involved in mining usually purchase or rent hardware from professional companies and join mining pools. Mining pools use the computational power provided by individual miners and create a big pool. With many miners, a pool has a greater chance of finding a coin, but the reward tends to be distributed among the members. The pool operator, a blockchain network administrator, manages mining activities and in accordance with the reward distribution strategy splits up the payments among the members.
Solo mining is also an option, however, as the field is becoming more advanced, technical and costly so is the process of starting up. Thus, individuals tend not to take on this journey single-handedly. Solo mining has its perks as whoever finds a coin claims all the rewards. But on the flip side, getting rewarded might be a challenge. If we examine the number of blocks that a miner can generate in the first year of her/his entrance in the industry, the variance is rather high, while the generated blocks pretty low.
Mining
Let’s move to the actual mining procedure. Broadly speaking, the mining process comprises of two distinct parts:
-
The one where transactions and blocks are validated
-
And the one where miners race to find the block and generate profit.
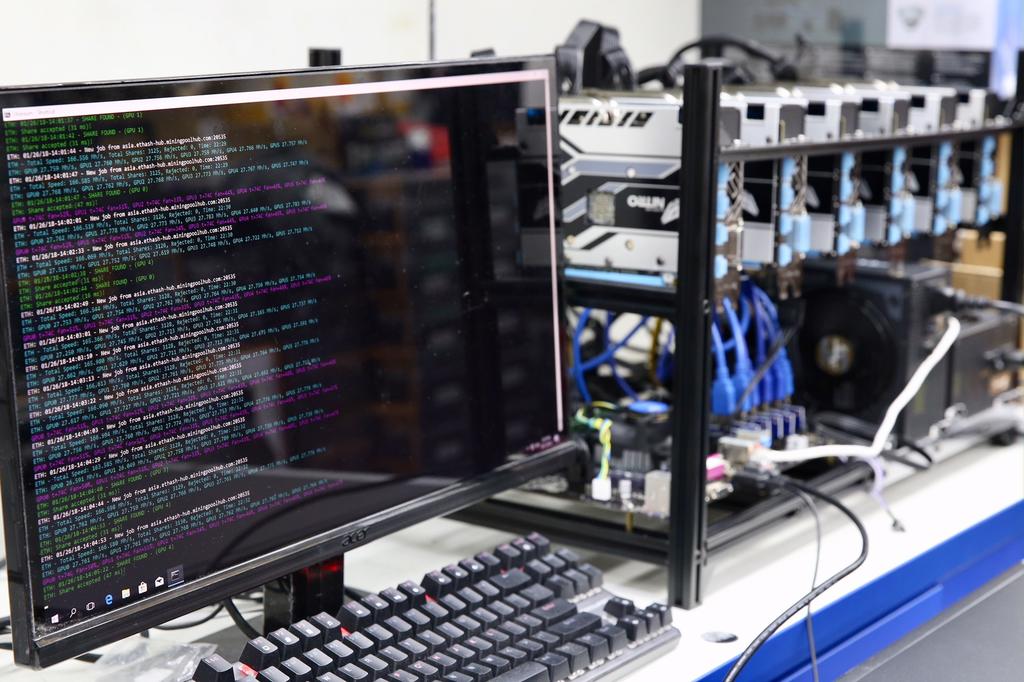

In order for the blockchain to function you only need the former fulfilled; somehow the second part is key in incentivizing miners to be part of the system and complete the above. This way both of the tasks are critical for the network to function as a cryptocurrency.
To dig deeper, let’s go over the six essential steps that need to be accomplished, after joining the Bitcoin network and connecting up with other nodes of the system:
-
Watch out for transactions — Miner should listen to transactions happening on the network and check for double-spending as well as for the valid signatures on the transfers.
-
Retrieve an up-to-date blockchain and listen for the new blocks that are broadcasted — Get the existing blockchain ledger from other nodes on the network and work on maintaining it.
-
Generate a candidate block — With a valid historical blockchain now miners can start assembling their own block by validating transactions and gathering them in one block that is an extension of the last block on the blockchain. To break it down a little bit more, first, they have to validate the transactions from the pool of pending transactions and then compile them in one block the header of which will contain a hash of the previous block and will point back at it. Thus, during this process mines are generating a Markle Tree of singular transactions and a block that contains all this data, which will eventually be placed on the blockchain ledger if approved by other miners.
-
Validate the generated block by finding an accurate nonce — The next step is validating the generated block, which is done by finding a correct nonce. The nonce resides in the header of the block and has 32 bits. Miners need to try different possible nonce values that could produce a valid hash for the block. Once they land the right combination the block will be fully prepared to be broadcast in the network to other nodes.
-
Be hopeful that the block gets accepted by other miners — Once the block is validated, it is advised to immediately announce the achievement. However, broadcasting the block does not always mean that it will be accepted by the network during the consensus process. Other miners might accept a block generated by another node and start building a new block on top of it. This might make you wonder how can another miner’s block be accepted over mine? Are all miners solving the same puzzle? The answer is no — not everyone’s block is identical. They might be sharing some transactions, however, it is highly unlikely all miners to include thr same transactions in their blocks. However, if we allow of such case, the puzzles will still not be identical because generated blocks contain public key of a miner, which will stand as a differentiator between the blocks.
-
Generate the cash flow! — If the nodes accept your block you will make a profit and earn 25 Bitcoins, which using the current exchange rate, is around 160,00 USD. In addition to this reward, the miner will also be receive another modest prize which is transaction fees contained inside the block.
Mining difficulty tends to increase as more blocks are added to the blockchain. For example, the difficulty of mining a bitcoin rises in every 2,016 blocks or in two weeks. This ensures that each block mining will take on average 10 minutes. As more miners enter the platform, the hash power increases and the time required to mine drops, thus increasing the level of difficulty in every 2 weeks ensures that this standard time that elapses between two consecutive blocks on the blockchain is adjusted and maintained.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency mining is embedded with misconceptions and stereotypes that need to be addressed. Mining has often been compared to the valuable metal mining, where amateurs get hyped with prospects of quickly accumulating wealth and, without much thought, rush to enter the market just to be sent back off empty-handed. It is up to your personal judgment to decide which path to take, however, It is crucial to understand all the drawbacks and benefits associated with the mining business in order to make an effective decision.
The next blog post will explore and discuss some other aspects of the mining, stay tuned!
Work Cited
[1] Narayanan, Arvind, Joseph Bonneau, Edward Felten, Andrew Miller, and Steven Goldfeder. Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Technologies: A Comprehensive Introduction. Princeton and Oxford: Princeton University Press, 2016.
比推快讯
更多 >>- 美股三大股指期货周一小幅高开
- 美联储 12 月降息 25 个基点概率为 86.2%,明年 1 月降息概率为 65.4%
- 数据:54.98 万枚 TRUMP 从 Official Trump Meme 转出,价值约 316.68 万美元
- 数据:过去 24 小时全网爆仓 3.43 亿美元,多单爆仓 2.24 亿美元,空单爆仓 1.19 亿美元
- 据比推数据,ETH现报3107.84美元,1小时涨幅为5.07%,价格波动较大,请谨慎交易,控制风险。
- 美财长贝森特:美国今年 GDP 增速将达 3%
- 1011 内幕巨鲸再次向 Hyperliquid 存入 1000 万枚 USDC,以 5 倍杠杆做多 9010.4 枚 ETH
- 数据:755.51 万枚 TRX 从 Binance 转出,价值约 214.88 万美元
- 数据:巨鲸 ETH 和 XRP 多单浮亏扩大至 2493 万美元
- 铁杆空头巨鲸的 20 倍杠杆 BTC 空单现浮盈超 2000 万美元
- 数据:7246.9 亿枚 PEPE 从 Coinbase 转出,价值约 314.52 万美元
- 麻吉割肉平仓 ETH 多单后再次做多 2100 枚 ETH
- K33 Research:市场大幅上涨可能性大于再次下跌,12 月或有建仓良机
- 特朗普计划以关税收入取代个人所得税
- Michael Saylor 再次发布比特币 Tracker 信息,或暗示再次增持 BTC
- Glassnode:比特币企稳后投资者恐慌情绪消退,资金开始流向看涨期权
- Ansem:比特币或将在 12 月再次测试 8 万美元
- Stable 代币上线首日后 FDV 超 20 亿美元概率升至 85%
- 某个疑似 Wintermute 钱包过去两周积累价值 520 万美元的 SYRUP 代币
- 马斯克回应 X 遭 1.2 亿欧元罚款:欧盟应该被废除
- 某新建钱包向 Hyperliquid 存入 300 万枚 USDC 开设 10 倍杠杆 HYPE 多单
- 分析:美 SEC 拟评估加密隐私与监管权重,监管走向或现两极化
- 中央网信办主任:提升区块链共性服务支撑能力,加快区块链等数智技术创新
- Pump.fun 过去 24 小时协议收入超越 Hyperliquid
- Crypto DAO 将于 12 月 10 日开启全球节点认购
- Paradigm 联创:此刻正是加密行业的Netscape 或 iPhone 时刻
- 哈塞特:美国将迎经济史上的黄金一年,除非有“黑天鹅”干扰
- Strategy CEO:公司的美元储备可支撑至少 21 个月无需出售比特币
- Strategy CEO:不存在无法履行股息义务问题,有人散播谣言
- 数据:过去 24h Binance 净流出 5.14 亿 USDT
- 法国银行巨头 BPCE 公布加密交易服务详情:现支持 BTC、ETH、SOL 和 USDC
- 币安更新 12 月储备金证明:BTC 储备率 102.11%,USDT 储备率 109.16%
- 21 Capital 因上市需要拟将 4.35 万枚比特币转至自主托管账户
- 加密 KOL:Binance Futures 官方账号推文与链上发币存在时间差,或涉及内幕交易
- Hasu 与 Vitalik 激辩链上 Gas 期货市场想法:做多意愿较弱将引发流动性不足,或难形成规模
- 数据:沉睡 13 年的 Casascius 实物币转移 2000 枚比特币,约合 1.8 亿美元
- Solana 基金会总裁呼吁生态借贷协议停止内斗、专注扩大市场
- 麻吉以太坊多单再次陷入浮亏,曾一度浮盈超 160 万美元,最新爆仓价 2,990.67 美元
- 数据:299.89 枚 BTC 从匿名地址转出,价值约 2289 万美元
- 数据:415.21 万枚 TON 从匿名地址转出,经中转后流入 TON
- 某巨鲸以 3,040.92 美元均价 2 倍做多 2 万枚 ETH
- 预测市场 DeFi 层协议 Gondor 完成 250 万美元 Pre-Seed 轮融资,Prelude 等参投
- OKX 创始人 Star 回应与摩尔线程联创李丰纠纷:债务交由法律处理,不应停留在负面阴影
- Kalshi 发布新 SDK,全面开放交易、行情与投资组合管理 API
- 分析师:CEX 平台 ETH 持有量降至 8.8% 历史低位,供应紧张或推动价格上涨
- 韩国拟要求加密交易所承担“无过错赔偿义务”,Upbit 遭黑客事件成导火索
- DOYR 代币 TOP1 持有者在上线 5 分钟内买入超 2,400 万美元,目前浮盈 19.3 万美元
- 摩尔线程联创李丰被曝曾涉发币、欠 1500 枚 BTC 不还
- 数据:当前加密恐慌贪婪指数为 21,处于极度恐慌状态
- 前交银香港高管叶子建:全力支持金融科技发展,抓紧数字货币等关键战略领域机遇
比推专栏
更多 >>观点
比推热门文章
- 美联储 12 月降息 25 个基点概率为 86.2%,明年 1 月降息概率为 65.4%
- 数据:54.98 万枚 TRUMP 从 Official Trump Meme 转出,价值约 316.68 万美元
- 数据:过去 24 小时全网爆仓 3.43 亿美元,多单爆仓 2.24 亿美元,空单爆仓 1.19 亿美元
- 美财长贝森特:美国今年 GDP 增速将达 3%
- 1011 内幕巨鲸再次向 Hyperliquid 存入 1000 万枚 USDC,以 5 倍杠杆做多 9010.4 枚 ETH
- 数据:755.51 万枚 TRX 从 Binance 转出,价值约 214.88 万美元
- 数据:巨鲸 ETH 和 XRP 多单浮亏扩大至 2493 万美元
- 铁杆空头巨鲸的 20 倍杠杆 BTC 空单现浮盈超 2000 万美元
- 数据:7246.9 亿枚 PEPE 从 Coinbase 转出,价值约 314.52 万美元
- 麻吉割肉平仓 ETH 多单后再次做多 2100 枚 ETH
 比推 APP
比推 APP








